Turn Your Process into a Plug-and-Play Robotic Solution.
◦ Universal real-time robots control
◦ Modular no-code software platform
◦ Standardized application robotic cells
◦ Automatic trajectory generation
Discover the Fuzzy Logic Automation Platform
A modular platform that makes robotics adapt to your process.
From programming to deployment, accelerate every step.
.jpg?quality=low&width=2000&height=1261&name=Visuel%20site%20(1).jpg)
Real Time Control
The Universal Real-Time OS for OEMs Integrating Robotics
Seamlessly add robotics to your specialized products—without being locked into a single robot brand or automation system.
Part to Path
Seamless CAD & Mesh-Based Tool Path Generation
Integrate tool path generation into your software—without spending months on development.
Sequencer
No-Code Robot Programming—For Any Robot, Any User
Create robotic workflows in minutes—without writing a single line of code.
Trajectory Generation
Real-Time Trajectory Generation—Optimized for Precision & Speed
Generate highly optimized, dynamically feasible trajectories—without compromising speed, accuracy, or safety.
Collision Detection
Prevent Costly Collisions—Validate Your Robot’s Motion in Seconds
Easily detect and prevent collisions before they happen—keeping your robots, tools, and workpieces safe.

Kinematics
The First Real-Time Kinematics Solver—Built for Any Robot
Integrate a high-performance FK/IK solver into your system—without reinventing the wheel.
Component Library
Pre-Built, Fully Interactive Robot Models—Ready for Your Software
Instantly integrate an ever-expanding library of robotic digital twins—without wasting months on development.
Coming soon:
- Calibration module
- AI module

Free licence for student
Use Fuzzy Logic platform, including modules, free of charge for the duration of your studies
Standard systems
Ready to use robotic systems for factories of any size.
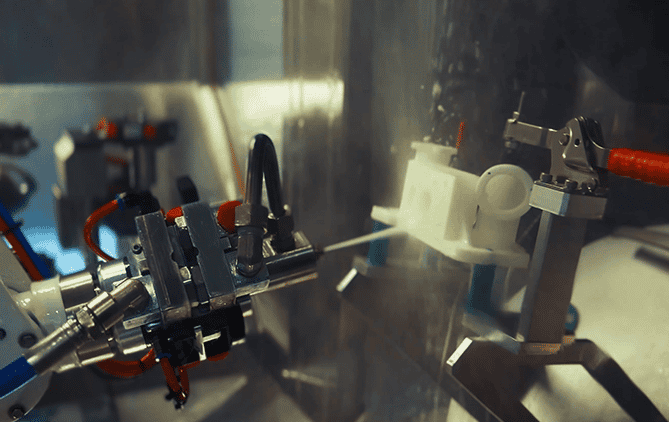
Automate Cleaning. Reduce Costs. Boost Efficiency.
Streamline industrial cleaning with powerful, adaptive automation and no-code programming—built for your toughest jobs.
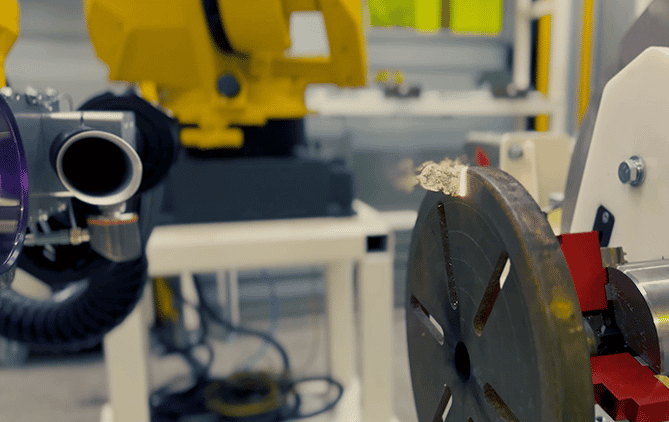
Effortless Robotic Laser Cleaning for Aerospace
Automate engine maintenance with precision, safety, and zero chemical waste—no robotics expertise required.

WeldMate: The €30,000 welding robot you don’t need to program.
Teach with a gesture, weld in minutes—no integration, no delays, no engineers required.


-1.png?width=1200&length=1200&name=Framatome%20(1)-1.png)


-1.png?width=1200&length=1200&name=Meliad%20(2)-1.png)

-1.png?width=1200&length=1200&name=ERM%20Automatismes%20(1)-1.png)
-2.png?width=1200&length=1200&name=Atol%20CD%20(1)-2.png)









